Understanding electrical panel components is essential for home safety and maintenance. In this article, you’ll learn about the main parts of an electrical panel, how they function, and why they matter.
Key Takeaways
- Electrical panels, often referred to as breaker boxes, are essential for safely distributing power throughout a home and preventing electrical hazards.
- Key components of an electrical panel include the main circuit breaker, individual circuit breakers, and bus bars, all playing vital roles in managing power distribution and protecting against overloads.
- Regular maintenance, including inspections and keeping the area around the panel clear, is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of your electrical system.
Understanding Electrical Panels
Electrical panels, often referred to as breaker boxes, are crucial for distributing power safely throughout a home. They prevent overloads and short circuits, ensuring that electricity flows smoothly to all your electrical devices. Typically installed in basements, storage rooms, or garages, these distribution panels serve as the brain of your home’s electrical system, including the electrical control panel and service panels. The main service panel, also known as the breaker box, is the central distribution point for the home’s electrical system.
Electricity flows from the utility company through power lines and the electrical meter before entering the home’s electrical panel. The main breaker in an electrical panel acts as the primary control for the electricity supply. It regulates power and ensures safe distribution throughout the house. Without understanding the components and functions of your electrical panel, you could face unexpected issues and potentially dangerous electrical fires.
The electrical panel supplies power to the entire house, and the panel door provides safe access to the breakers and components inside. A solid understanding of your home’s electrical panel ensures safe operation and efficiency of your home’s electrical system, empowering you to troubleshoot minor issues and recognize when to call a professional for serious problems regarding the right electrical panel and the electrical control panel. Knowing your home’s electrical service capacity is essential for safety and future upgrades.
Fuse Box vs Electrical Panels
When it comes to managing electrical power in your home, understanding the difference between a fuse box and an electrical panel is essential. Both systems are designed to distribute electrical power and protect electrical circuits from overloads, but they operate in distinct ways.
A fuse box, sometimes called a fuse panel, uses fuses as protective devices. When too much electrical current flows through a circuit, the fuse melts and breaks the circuit, stopping the flow of electricity and helping to prevent electrical fires. However, once a fuse blows, it must be replaced before the circuit can be used again.
In contrast, modern electrical panels—also known as circuit breaker panels—use circuit breakers to protect electrical circuits. Circuit breakers automatically switch off the power supply to a circuit when they detect an overload or short circuit. Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be easily reset after they trip, making them more convenient and cost-effective for ongoing electrical panel work.
Electrical panels with circuit breakers offer several advantages over fuse boxes. They provide enhanced safety features, are better equipped to handle the higher electrical loads of today’s homes, and are more adaptable to modern electrical systems. Circuit breaker panels also make it easier to protect electrical circuits and reduce the risk of electric shock and electrical fires.
For these reasons, electrical panels are the preferred choice for new homes and electrical system upgrades. If your home still uses a fuse box, it may be time to consider upgrading to a circuit breaker panel for improved safety, efficiency, and peace of mind.
Main Components of an Electrical Panel
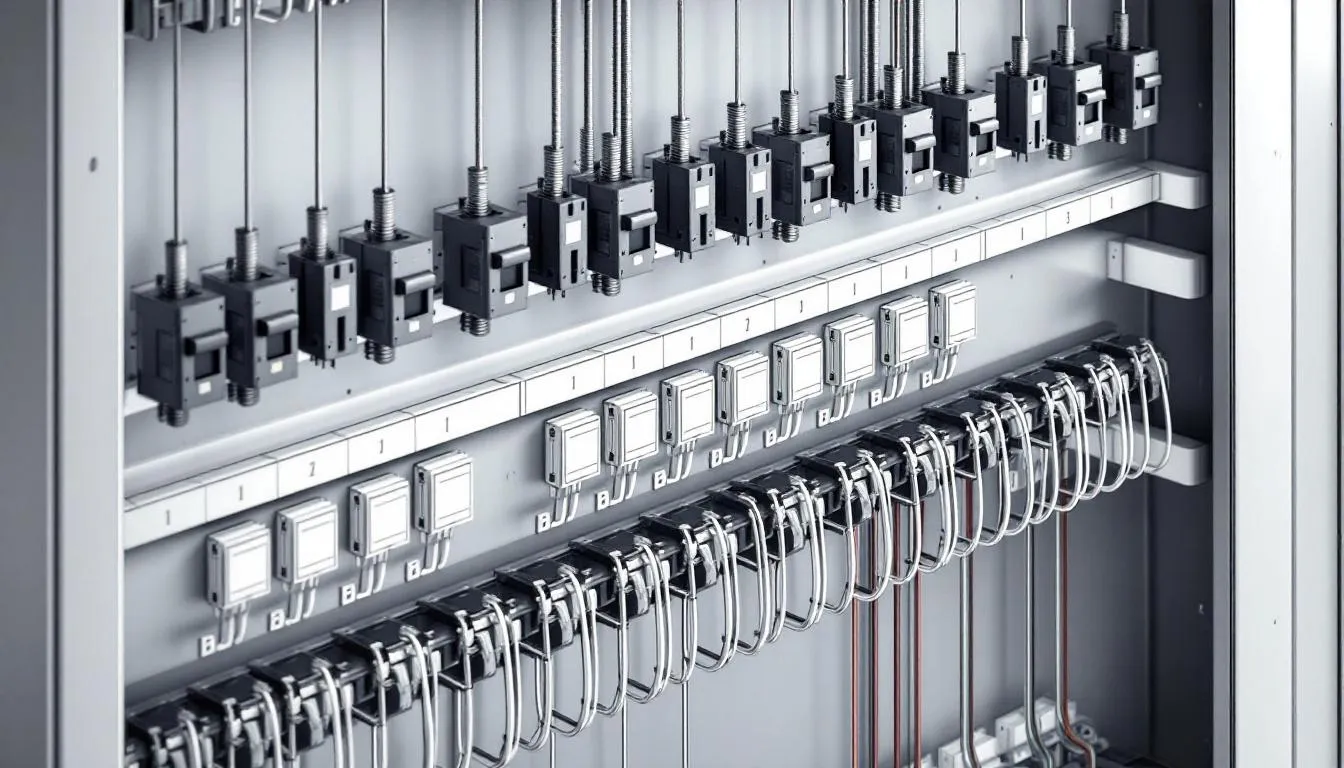
The electrical panel is composed of several crucial components, each playing a vital role in the system’s functionality:
- The main circuit breaker controls power to all the branch circuits, protecting against electrical overloads.
- Individual circuit breakers, also known as breaker switches, can be manually operated to control individual circuits. Each breaker controls a different circuit, allowing for localized management of individual circuits and preventing overloads.
- Bus bars and wires carry electricity from the main source and are essential for conducting and distributing electrical power to various circuit breakers and different circuits.
Terminal blocks are also used within the panel to organize and connect multiple wires, facilitating wiring connections and efficient distribution of electricity.
Knowing these key components and essential components helps maintain a safe and efficient electrical system.
Main Circuit Breaker
The main circuit breaker controls the main electrical panel, handling the total load of all the home’s circuits. It can shut off power to the entire house, providing a critical safety feature for quickly stopping electricity flow in emergencies. Additionally, the main breakers play a vital role in managing the overall electrical system, including the main panel.
If the main breaker trips due to high power demand or a power surge, it protects the system from potential damage. This feature is essential, as it ensures that if an individual circuit breaker fails to trip, the main breaker steps in to prevent overloads and electrical hazards.
Knowing the role of the main circuit breaker ensures the safety and functionality of your home’s electrical system.
Individual Circuit Breakers
Individual circuit breakers play a crucial role in preventing excessive current in electrical circuits, thereby protecting appliances and wiring. Each breaker is designed to safeguard specific circuits from overload and faults, including those caused by arc-fault circuit interrupters, ensuring safety and reducing electrical hazards. These breakers trip to interrupt the flow of electricity, preventing potential damage to the electrical system.
It is important to note that multiple devices plugged into different outlets may still be on the same circuit. If too much current is drawn by devices sharing the same circuit, it can lead to overloads and cause the breaker to trip.
Typical electrical panels can accommodate between 4 to 42 circuit breakers, with sizes ranging from 15 to 200 amps, most commonly 15, 20, or 30 amps. Circuit breakers come in different types, providing various voltage levels: single-pole circuit breakers provide 120 volts, while double-pole circuit breakers provide 240 volts.
Knowing the types and sizes of circuit breakers aids in managing the electrical load efficiently.
Bus Bars
Bus bars are essential for conducting and distributing electrical power from the main source to various circuit breakers. These thick metal strips, made of materials such as copper, brass, or aluminum, play a crucial role in the electrical panel’s functionality. They ensure a stable and efficient distribution of power throughout the system.
Bus bars distribute power from the main breaker to circuit breakers, enabling the smooth flow of electricity to different circuits. Recognizing the function and importance of bus bars maintains an efficient and safe electrical system.
Additional Components Ensuring Safety and Functionality
In addition to the main electrical components, electrical panels include several panel components and other devices that ensure safety and functionality. These include the neutral bar, ground bar, and bonding jumper. Terminal blocks are also used to organize and consolidate wiring connections within the panel, making management and troubleshooting easier. Modern panels often include ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) to protect against ground faults, which occur when a hot wire contacts a grounded object. GFCIs immediately cut off power when a ground fault is detected, especially in areas like bathrooms or kitchens where water increases the risk.
Understanding these additional electronic components helps in ensuring the overall safety of your protective device’s electrical system, including structural components.
Neutral Bar
The neutral bar completes electrical circuits and allows current to return to the utility grid. It is essential for routing current back to the source after it has powered devices, ensuring the continuous flow of electricity. Neutral wires are usually color-coded white or gray, which helps in distinguishing them from hot wires.
Neutral wires play a crucial role in completing the electrical circuit by returning current to the source. Recognizing the function and importance of the neutral bar is vital for a safe and efficient electrical system.
Ground Bar
The ground bar and grounding wires play crucial roles in electrical safety:
- The ground bar is connected to grounding wires for safety.
- It directs unwanted electrical currents safely into the ground.
- This enhances the safety of the electrical system by providing a path for stray electrical current during faults.
- Grounding wires, identifiable by their green insulation, provide a safety path for electrical current.
- They direct electrical current safely into the ground during faults.
Grounding wires are usually bare copper or green, indicating their primary role in safety and fault protection. The grounding system protects against electrical surges by allowing stray electrical current to pass safely into the surrounding soil.
Recognizing the function and importance of the ground bar is vital for a safe and efficient electrical system.
Bonding Jumper
The main bonding jumper connects the neutral bars to the service panel. It also connects the ground bars to the same panel. This connection is crucial for creating a safe electrical connection between the neutral and ground systems, ensuring the overall safety of the electrical panel.
By understanding the function and importance of the bonding jumper, you can ensure that your electrical system operates safely and efficiently, preventing potential hazards like short circuits and electrical fires.
Wiring and Connections

Wiring connections in an electrical panel are essential for connecting individual circuit breakers to specific outlets or multiple appliances. These connections ensure that the electrical current is distributed efficiently throughout the home, enabling effective power distribution and electrical supply to various devices and appliances, which helps to protect electrical circuits.
Knowing the types of wiring connections and their importance maintains a safe and efficient electrical system.
Hot Wires
Hot wires are responsible for carrying live electrical current to circuits, enabling the distribution of electricity throughout the home. These electrical wires power various appliances and devices, ensuring that your home functions smoothly. A hot wire is typically insulated with a black or red coating to help identify its function in the system, especially when dealing with multiple wires.
Knowing the role and identification of hot wires helps maintain the safety and efficiency of your electrical system, preventing hazards like electric shock and short circuits.
Neutral Wires
Neutral wires play a crucial role in electrical systems, serving to return current to the panel and ensure the proper functioning of circuits. These wires complete the circuit by returning current to the source, allowing for the continuous flow of electricity. Returning electrical current to the panel is essential for the safe and efficient operation of the electrical system.
Recognizing the function and importance of neutral wires maintains a safe and efficient electrical system, preventing hazards like short circuits and electrical fires.
Grounding Wires
Grounding wires:
- Offer an alternate path for electrical current in case of a fault, guiding stray current safely into the ground.
- Reduce the risk of electric shock and enhance the safety of the electrical system.
- Direct electricity into the ground, preventing potential hazards like electrical fires and short circuits.
Knowing the role and importance of grounding wires maintains a safe and efficient electrical system, ensuring home safety.
Capacities of Electric Panels for Homes
The capacity of your main electrical panel is a crucial factor in ensuring your home’s electrical system can safely handle your power needs. Electric panels are rated by the maximum amount of electrical current they can manage, typically measured in amps—common sizes include 100, 150, 200, or even 400 amps.
Choosing the right capacity for your circuit breaker panel depends on several factors, such as the size of your home, the number of electrical devices and appliances you use, and your overall electrical load. For example, a 200-amp main electrical panel is standard in many modern homes, as it can support multiple appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems without frequent breaker trips. Smaller homes with fewer electrical devices may only require a 100-amp panel.
Selecting an electric panel with insufficient capacity can lead to overloaded circuits, frequent breaker trips, and even electrical fires. On the other hand, a panel with the right capacity ensures safe, efficient power distribution and allows for future expansion if you add more appliances or upgrade your home.
To determine the appropriate capacity for your electrical panel, it’s best to consult a licensed electrician. They can assess your current and future electrical needs, ensuring your main electrical panel delivers reliable electrical power to all areas of your home.
Factors to Consider While Buying an Electrical Panel
Selecting the right electrical panel is essential for the safety, efficiency, and reliability of your home’s electrical system. When buying an electrical panel, start by evaluating your total electrical load—the combined power requirements of all your electrical devices, appliances, and lighting. Make sure the panel you choose can handle both your current needs and any future additions.
Consider the types of circuit breakers the panel supports. Standard circuit breakers protect against overloads, while arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs) and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) offer additional protection against electrical fires and electric shock. Choose a panel that accommodates the right mix of breakers for your home’s safety.
Compatibility with your existing electrical system is also important. Ensure the panel matches your home’s voltage and frequency requirements, and that it fits the available space. Think about the number of circuits you’ll need, the type of wiring in your home, and the location of the panel for easy access and maintenance.
Always check that the electrical panel meets local electrical codes and standards, such as the National Electric Code (NEC). It’s wise to choose a reputable manufacturer, review warranty options, and consider the overall cost, balancing quality and budget.
By carefully considering these factors, you’ll select an electrical panel that provides safe, efficient power distribution and supports the long-term needs of your electrical system.
Mapping Your Circuits
Creating a circuit map for your electrical panel is a simple yet powerful way to improve the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. A circuit map, or circuit directory, is a chart or diagram that shows how electrical power is distributed to different circuits, including which circuit breakers control which electrical devices and outlets.
To map your circuits, identify each branch circuit in your electrical panel and label the corresponding circuit breaker. Note the rooms, outlets, lighting, and major appliances connected to each breaker. This process helps you quickly locate the right circuit breaker when you need to perform maintenance, reset a breaker, or troubleshoot electrical issues.
Having a clear circuit map also helps prevent electrical overloads by making it easy to see which circuits are powering multiple appliances or devices. This can reduce the risk of electrical fires and ensure your electrical panel is not overloaded. Additionally, a circuit map is invaluable when adding new electrical devices, as it helps you determine which circuits have available capacity.
By taking the time to map your circuits, you’ll make your electrical panel work more efficiently and ensure safer power distribution throughout your home.
Signs of Electrical Panel Issues

Recognizing the signs of electrical panel issues is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. Frequent tripping of breakers, warm or discolored panels, and strange noises or smells are common indicators of potential problems. Malfunctioning breaker switches can also signal panel issues and may require testing or replacement.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more serious hazards like electrical fires and costly repairs.
Frequent Tripping of Breakers
Frequent tripping of breakers indicates overloading of the electrical panel and may signal underlying issues in the electrical system. A tripped breaker indicates that circuits may be overloaded, which is a common cause of frequent breaker trips. Proper load management is essential to prevent frequent tripping and ensure the safety of the electrical system.
Homeowners may need to upgrade their electrical panel if frequent trips occur, especially due to an insufficient power supply. Adding subpanels or tandem circuits is are potential solution for insufficient capacity in an electrical panel. Knowing the importance of proper load management maintains an efficient and safe electrical system.
Warm or Discolored Panel
A warm or discolored electrical panel suggests that the circuits are overheating, which can pose a fire risk. Overheating circuits can lead to an electrical fire, which poses a significant risk to homes and safety. Homeowners should immediately turn off the power to the panel and seek professional assistance if they notice signs of overheating, especially if they have outdated electrical panels.
Addressing overheating issues promptly ensures the safety and efficiency of your electrical system, preventing hazards like electrical fires.
Strange Noises or Smells
Unusual sounds from the electrical panel indicate problems with wiring or panel overloading. Strange noises or smells coming from the electrical panel require immediate attention. Addressing these issues promptly can prevent more serious hazards like electrical fires and costly repairs.
Addressing strange noises or smells promptly ensures the safety and efficiency of your electrical system, preventing hazards like electrical fires.
Upgrading and Repairing Your Electrical Panel
Upgrading or repairing your electrical panel is a critical step in maintaining a safe and reliable electrical system. The main electrical panel is the heart of your home’s power distribution, and issues such as outdated electrical panels, frequent breaker trips, or increased electrical demands can signal the need for professional attention.
Common reasons for upgrading include adding new appliances, renovating your home, or replacing a fuse box with a modern circuit breaker panel. Repairs may be necessary if you experience problems like breaker trips, flickering lights, or signs of wear and tear.
Always hire a licensed electrician for electrical panel work. A professional will assess your current electrical system, recommend the right upgrades or repairs, and ensure your new or repaired panel meets all local codes and safety standards. This may involve installing a new main electrical panel, upgrading circuit breakers, or adding additional circuits to support your electrical load.
Upgrading your electrical panel not only improves safety and reduces the risk of electrical fires, but also increases your home’s capacity to handle modern electrical devices and future expansions. Investing in a reliable, up-to-date electrical panel ensures your home’s electrical system remains safe, efficient, and ready for whatever the future holds.
Maintaining Your Electrical Panel

Regular maintenance of electrical panels can help prevent dangerous situations like flickering lights and electrical fires. Homeowners can conduct basic inspections of their panels and manage, but they should hire a certified electrician for electrical work or enhancements.
Regular maintenance ensures the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system.
Regular Inspections
Professional inspections of electrical panels should occur approximately every three to five years. During these thorough inspections, professionals assess the condition of breakers and connections and may perform thermal checks to identify any potential issues. Regular inspections help identify and fix potential issues early, ensuring safety and optimal performance of the electrical system.
Conducting regular inspections minimizes risks associated with electrical failures and enhances the longevity of the electrical system. This proactive approach ensures that your electrical panel remains in good condition, preventing potential hazards like electrical fires and costly repairs.
Keeping the Area Around the Panel Clear
It is essential for safety to keep the area around the electrical panel clear. This also contributes to efficiency. A clear access area around the electrical panel is crucial because:
- It ensures that you can quickly and safely access the panel in emergencies.
- It allows professionals to perform maintenance and inspections without obstructions.
- It enhances the overall safety and functionality of the electrical system.
Keeping the area around the panel clear maintains a safe and efficient electrical system, preventing hazards like electrical fires and ensuring home safety.
Summary
Understanding the components and functions of your electrical panel is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficiency of your home’s electrical system. From the main circuit breaker to individual circuit breakers, bus bars, and additional components like the neutral bar, ground bar, and bonding jumper, each part plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth flow of electricity and preventing potential hazards.
Regular maintenance, including professional inspections and keeping the area around the panel clear, can help prevent dangerous situations and enhance the longevity of your electrical system. By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure that your electrical panel remains in good condition, providing reliable and safe power distribution throughout your home.
In industrial settings, control panels and electrical control panels house essential control devices and manage complex industrial systems, ensuring operational safety and efficiency. Panels manage various electrical devices and processes in both residential and industrial environments, serving as central hubs for effective system control.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of the main circuit breaker?
The primary function of the main circuit breaker is to control the total load of all circuits in a home and to shut off power to the entire building when necessary. It acts as a crucial safety measure for managing electrical flow.
How often should professional inspections of electrical panels be conducted?
Professional inspections of electrical panels should be conducted every three to five years to ensure safety and optimal performance. Regular inspections help prevent potential hazards and maintain the integrity of the electrical system.
What should I do if my electrical panel is warm or discolored?
If your electrical panel is warm or discolored, it indicates overheated circuits, which can pose serious risks. It is crucial to turn off the power immediately and consult a qualified professional to address the issue.
Why is it important to keep the area around the electrical panel clear?
It is crucial to keep the area around the electrical panel clear for safety and efficiency, as it allows for quick access during emergencies and facilitates maintenance by professionals without obstructions.
What are the signs of electrical panel issues that I should look out for?
Frequent tripping of breakers, warm or discolored panels, and unusual noises or smells are clear signs of electrical panel issues. Timely attention to these symptoms is crucial to avoid potential hazards such as fires and expensive repairs.

